Digital Communication - Quantization Strategy
Overview
The digitization of analog signals involves the rounding off of the values which are approximately equal to the analog values. The method of sampling chooses a few points on the analog signal and then these points are joined to round off the value to a near stabilized value. Such a process is called as Quantization.
A/D Conversion
- Sampling: sample the amplitude, horizontal(enough samples)
- Quantization; assign the samples to a level, vertical(enough bit-depth per sample)
- Encoding: binary code for transmission, voltage pass through hardware
Quantization
Quantization is representing the sampled values of the amplitude by a finite set of levels, which means converting a continuous-amplitude sample into a discrete-time signal.
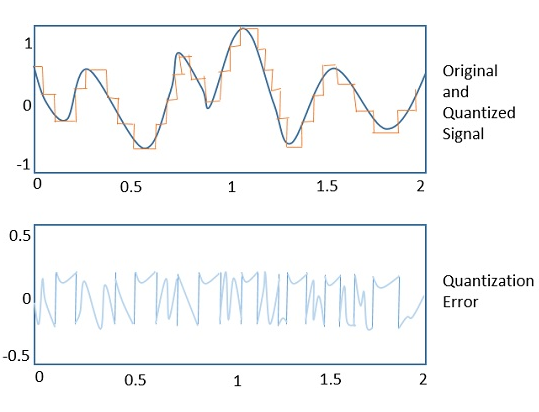
The following figure shows the process of an analog signal gets quantized. The blue line represents analog signal while the brown one represents the quantized signal.
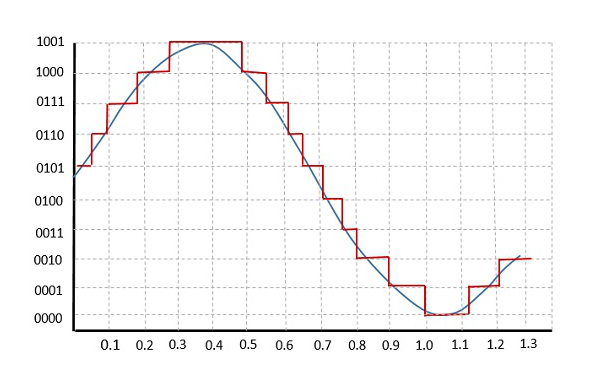
The quality of a Quantizer output depends upon the number of quantization levels used. The discrete of the quantized output are called as representation levels or reconstruction levels. The spacing between the two adjacent representation levels is called a quantum or step-size.
Quantization Error
The difference between an input value and its quantized value is called a Quantization Error.
A Quantizer is a logarithmic function that performs Quantization roundingoffthevalue.
An analog-to-digital convert(ADC) works as a quantizer.